Table Of Content

The best way to prevent ingrown hairs is to avoid shaving and waxing. If a person wants to remove hair, it may help to switch to a hair removal cream or laser treatment. In cases of bacterial infection resulting from the ingrown hair bumps on scrotum, your doctor may prescribe a topical or oral antibiotics. At times, the bumps could be infected causing them to become painful and itchy.
Coarse or curly hair
Picking at the hair can increase the risk of an infection spreading or worsening. If the infection becomes severe, a doctor may recommend antibiotics or other treatment. If you often develop infected ingrown hairs, the doctor may take a skin sample for testing. That’s why some ingrown hairs develop white pus-filled bumps on the surface. The infection can cause additional irritation and soreness.
Skin Tags on Anal Area – Pictures, Causes, Treatment & How to Get Rid
An ingrown pubic hair cyst is usually no cause for concern. A person may choose to have a cyst drained, or a doctor may make a small incision to free the trapped hair. An ingrown hair is a common cause of a pimple on the scrotum. This happens when a hair twists and grows back into the skin.
Draining the bumps
If you can’t figure out the difference between a pimple and cystic ingrown hair, you must know there are only a few sites where hair ingrowth can occur. Baking soda past has a soothing effect on skin due to its strong anti-inflammatory properties. When applied on an ingrown hair, it will help reduce itching by exfoliating the skin and also reducing redness caused by the ingrown hair.
Genital herpes
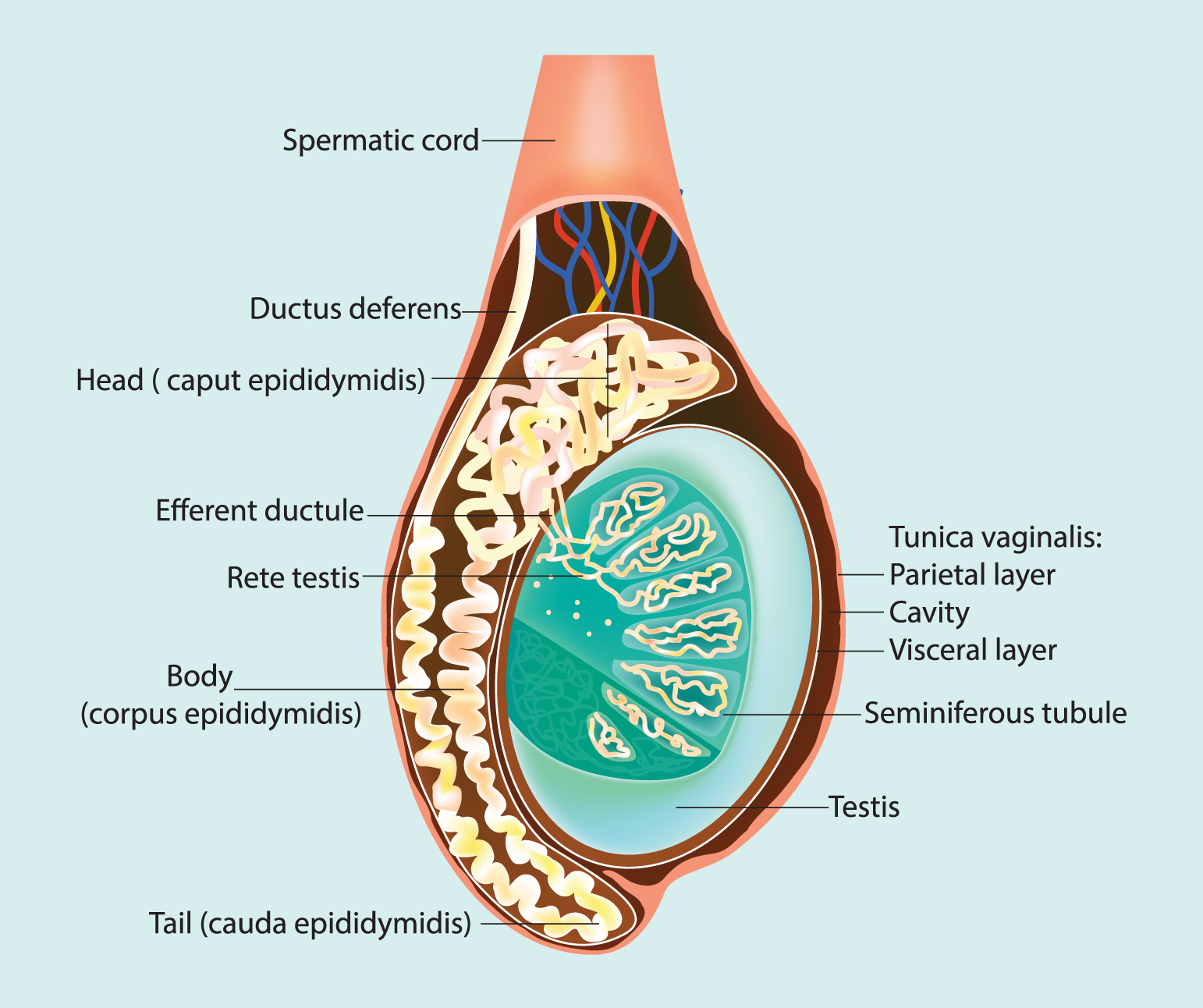
A spermatocele happens when a cyst grows in the epididymis, a tube in each of your testicles that contains fluid and unused sperm. It doesn’t cause any pain, but you can feel a spermatocele as a tiny, firm lump underneath the skin of the scrotum. Healthcare professionals can prescribe different medications that may ease severe symptoms and treat the infection.

Over time, an ingrown hair may develop into a cyst — a sac of fluid beneath the skin. Sweat and moisture often build up the groin area and clog pores, leading to pimples. White spots that appear on your testicles aren’t always a cause for concern. If your symptoms last longer than a week or two, see a doctor or other healthcare professional for a diagnosis.
Doctors thought he just had jock itch. Then it spread - New Zealand Herald
Doctors thought he just had jock itch. Then it spread.
Posted: Wed, 26 Oct 2016 07:00:00 GMT [source]
A warm compress will increase blood flow to your scrotum, which will help reduce the pain—especially if you’ve recently plucked the offending hair. You can try to pluck the hair if the ingrown hair is visible. We will warn you that this method is pretty painful, and you need to be extra careful to avoid unnecessary damage to the skin.
Shaving
Ingrown hairs are also known as razor bumps, shave bumps, ingrown hair bumps, or barber bumps. When hair follicles are damaged, they may be invaded by viruses, bacteria and fungi. Superficial folliculitis affects the upper part of the hair follicle and the skin around the follicle.
It can leave the shaved hairs primed to grow sideways or upside down into the skin. Squeezing an ingrown hair will increase the risk of infection. If an infection is present, squeezing the bump may worsen it.
If your condition doesn’t improve within a week, talk with a healthcare professional. They may recommend prescription antibiotics, such as cephalexin (Keflex) or doxycycline (Vibramycin). These cysts typically form in areas of dense hair, like your scalp or scrotum, and often appear in clusters.
Untreated boils may require professional medical treatment and can leave dark scars on the skin. To reduce the chances of getting ingrown hair cysts, keep your skin clean and gently exfoliated and moisturized. If you do shave, don't shave too close, and always shave in the direction the hair grows. Avoid squeezing ingrown pubic hair cysts, as it can damage the skin and increase the risk of scarring.
On your scrotum, pimples may look like a collection of tiny bumps in one area or even all around the thin scrotum tissue. You might have small bumps with hairs in the middle of your face and neck or on other hairy places on your body. They can be small, swollen bumps where you shave, tweeze, or wax. It is also important to avoid shaving too close, as this can make it easier for bacteria to enter the skin.
It is however not uncommon to have the cyst develop on the scrotal sack. The scrotum is the pouch of skin containing the testicles. It is an anatomical structure that consists of a suspended sack of skin and smooth muscle that is dual-chambered. The sac is common in most terrestrial male mammals and is located under the penis. You can try using some topical treatments—either over-the-counter or prescription from your provider—to help with healing. Natural antimicrobials like tea tree oil can also be helpful.
This will help prevent the chances of an infection or scarring. If you have chronic ingrown hair problems, it might be best to avoid shaving altogether. Instead, consider permanent ways to remove hair, like laser treatments or electrolysis. Although quite not permanent, depilatory methods, which include liquid or cream treatments like Nair, can produce long-lasting results as well. If your ingrown hair has looped or curled back into your skin, you can remove it by gently pulling it out with a sterile needle, pin, or tweezers. Use rubbing alcohol on the area to prevent an infection.
People with high levels of certain sex hormones can have more hair than usual. This can make you more likely to get ingrown hairs, especially after shaving. If the ingrown hair is near the surface of the skin, a person may be able to use sterile tweezers to gently pull the hair out.
Exfoliating your skin will help remove the buildup of dead skin cells and oil, which allows a better path for the hair to grow. The best way to prevent ingrown pubic hairs is not to shave or wax the area. Typically, lumps or cysts from ingrown hairs resolve independently.














